Behaviorism explains why we form our worldviews the way we do, mainly through environmental interaction.
Social Learning Theory says that we can combine thinking and conditioning to develop behaviors and attitudes about ourselves and others. In other words, we learn our behaviors from society and react accordingly.
Ivan Pavlov introduced the concept of classical conditioning by using dogs and food.
Stimulus Generalization is the response that comes from associating similar stimuli with a conditioned stimulus
Extinction is the disassociation of the conditioned response with a conditioned stimuli.
John Watson proved conditioning works on humans as well as animals through the "Little Albert" experiment.
- Behaviorists believe it is more important to focus on observable actions instead of thoughts.
- The combination of stimulus and response are used to interpret interactions between a person and his/her environment.
- A stimulus is an object or even that causes a reaction or response externally
- A response is the reaction to a stimulus.
Social Learning Theory says that we can combine thinking and conditioning to develop behaviors and attitudes about ourselves and others. In other words, we learn our behaviors from society and react accordingly.
Ivan Pavlov introduced the concept of classical conditioning by using dogs and food.
- Classical conditioning seeks to control involuntary responses.
- Pavlov knew that a dog would salivate at the sight of food, but taught the dog to salivate at the sound of a bell.
Stimulus Generalization is the response that comes from associating similar stimuli with a conditioned stimulus
- A doorbell or alarm could cause salivation, in the case of Pavlov's dog.
Extinction is the disassociation of the conditioned response with a conditioned stimuli.
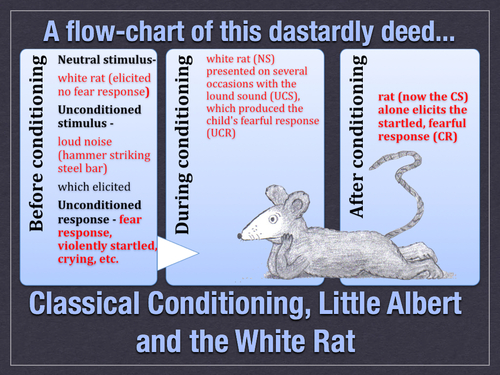
John Watson proved conditioning works on humans as well as animals through the "Little Albert" experiment.

Mary Jones explored an the irrational fear of objects, also known as phobias. Jones implemented counter-conditioning, which helped Little Albert overcome the fear of rats by repeatedly introducing him to the rat absent the noise of the hammer. This disassociated the rat from the noise, and eventually cured the fear.
BF Skinner introduced operant conditioning.
BF Skinner introduced operant conditioning.
- Operant conditioning seeks to control voluntary response.
- Skinner used conditioning with pigeons to teach that a response can be learned by use of positive and negative reinforcement.
- Positive reinforcement is something good that happens after a desired behavior.
- Negative reinforcement is taking away something undesired after a positive behavior.

Punishment is anything that might weaken the likelihood that a behavior will continue.
Continuous reinforcement is when a reward occurs every time a behavior occurs, thus a person expects it. This is good when a person is learning a new behavior, but doesn't enforce long-lasting results.
Intermittent Reinforcement is when a reward only occurs sometimes, thus a person isn't always aware of behavioral change. This type of reinforcement is good for the longevity of behavior.
Observational Learning is when people gain knowledge about what's appropriate through observation. This adds a mental and internal aspect to the external behaviorist perspective.
Julian Rotter believed that the life experiences a person has in various contexts impacts his/her beliefs which therefore influences behavior.
- Punishment I is adding an unfavorable event/outcome in order to weaken a behavior. For example, spanking a child after he leaves his toys out. This hopes to diminish the behavior of leaving the toys out.
- Punishment II is removing something good to decrease a behavior.
Continuous reinforcement is when a reward occurs every time a behavior occurs, thus a person expects it. This is good when a person is learning a new behavior, but doesn't enforce long-lasting results.
Intermittent Reinforcement is when a reward only occurs sometimes, thus a person isn't always aware of behavioral change. This type of reinforcement is good for the longevity of behavior.
Observational Learning is when people gain knowledge about what's appropriate through observation. This adds a mental and internal aspect to the external behaviorist perspective.
Julian Rotter believed that the life experiences a person has in various contexts impacts his/her beliefs which therefore influences behavior.
- Behavior potential is how likely someone is to do something, given a time and place.
- Expectancy is the belief that when someone demonstrates a particular behavior, it will lead to a specific outcome.
- Reinforcement value is the value placed on various outcomes. For instance, when someone places a high value on a good outcome and a low value on a bad one.
- Psych situation is how a person analyzes and makes conclusions about events in the environment.
- Locus of Control refers to how much control a person has over an outcome. With the internal locus, the person controls the outcome. With the external locus, the environment controls the outcome.
Albert Bandura developed the social cognitive theory. Within this theory he explored modeling, vicarious learning, self-efficacy and learned helplessness.
Personally >
I have been a violinist for twenty years, yes I started playing when I was three! Although I didn't realize it at the time, conditioning was a huge part of practice and lessons. The focus of my practice was repetition, repetition, repetition. When I was performing a technique the wrong way, my teacher would use an unconditioned stimuli, such as placing a hand over my hand to control the placement, over and over again until the technique was remedied. I did not like the hand on my hand, it got in the way of my playing! So I learned to place my finger where it was supposed to go, which removed the hand, but the desired behavior remained.
In the Future >
Conditioning and counter-conditioning can be used in the classroom to help children overcome a fear associated with a classroom setting. Many children have anxiety in regards to working math problems in front of a class, or reading out loud. Often this is not a reflection on the skill level, but a negative connotation associated with a bad experience. Teachers have a responsibility to provide a comfortable learning environment for each student, and this can begin with counter-conditioning to remove fear from learning.
- Modeling is imitation, but within that simplicity it is also adding and subtracting from learned behavior.
- Attention: people must be attentive to learn.
- Retention: people much have the ability to remember and reproduce observed behavior.
- Reproduction: people must have the ability to demonstrate observed action.
- Motivation: people must have a drive or enthusiasm to repeat the observed action.
- Vicarious learning is when individuals learn by observing the actions and consequences of others.
- Self-efficacy is how people perceive their ability to act for designated results.
- Learned helplessness is when a person responds passively to an adverse stimulus, which allows the stimulus to be in control.
Personally >
I have been a violinist for twenty years, yes I started playing when I was three! Although I didn't realize it at the time, conditioning was a huge part of practice and lessons. The focus of my practice was repetition, repetition, repetition. When I was performing a technique the wrong way, my teacher would use an unconditioned stimuli, such as placing a hand over my hand to control the placement, over and over again until the technique was remedied. I did not like the hand on my hand, it got in the way of my playing! So I learned to place my finger where it was supposed to go, which removed the hand, but the desired behavior remained.
In the Future >
Conditioning and counter-conditioning can be used in the classroom to help children overcome a fear associated with a classroom setting. Many children have anxiety in regards to working math problems in front of a class, or reading out loud. Often this is not a reflection on the skill level, but a negative connotation associated with a bad experience. Teachers have a responsibility to provide a comfortable learning environment for each student, and this can begin with counter-conditioning to remove fear from learning.